Microsoft Manager Mac
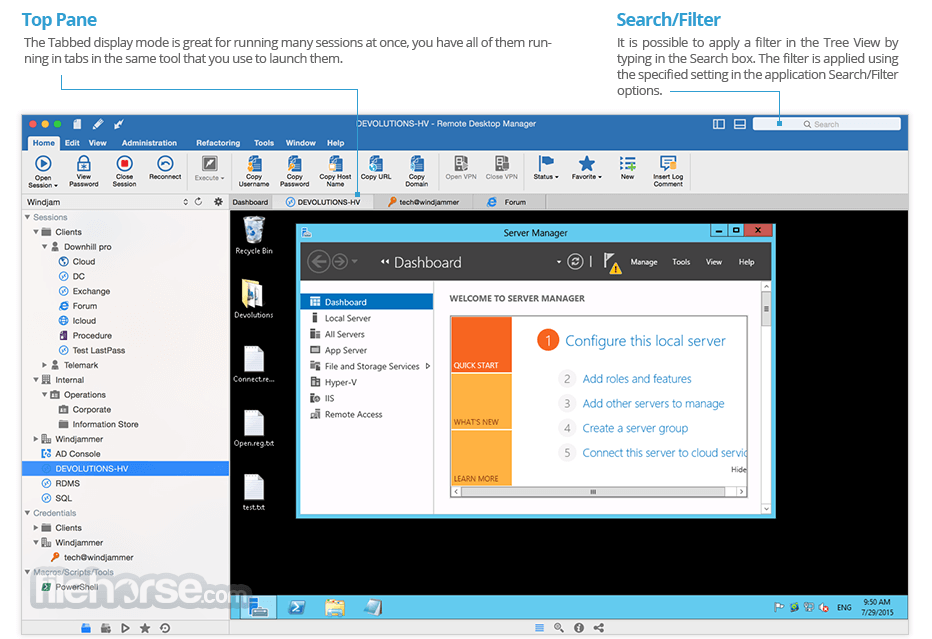
Use the Visual Studio debugger to quickly find and fix bugs across languages. The Visual Studio for Mac debugger lets you step inside your code by setting Breakpoints, Step Over statements, Step Into and Out of functions, and inspect the current state of the code stack through powerful visualizations. Easily manage your Azure storage accounts in the cloud, from Windows, macOS, or Linux, using Azure Storage Explorer. Azure Storage Explorer – cloud storage management Microsoft Azure Skip Navigation.
- Microsoft Update Manager Mac
- Microsoft Picture Manager Mac Download
- Microsoft Manager Mac Free
- Microsoft Customer Manager Mac
- Microsoft Office Picture Manager Mac
- Microsoft Picture Manager Mac Free Download
- Microsoft Mac Software
vcpkg is a command-line package manager for C++. It greatly simplifies the acquisition and installation of third-party libraries on Windows, Linux, and MacOS. If your project uses third-party libraries, we recommend that you use vcpkg to install them. vcpkg supports both open-source and proprietary libraries. All libraries in the vcpkg Windows catalog have been tested for compatibility with Visual Studio 2015, Visual Studio 2017, and Visual Studio 2019. Between the Windows and Linux/MacOS catalogs, vcpkg now supports over 1900 libraries. The C++ community is adding more libraries to both catalogs on an ongoing basis.
Simple yet flexible
With a single command, you can download sources and build a library. vcpkg is itself an open-source project, available on GitHub. It's possible to customize your private vcpkg clones in any way you like. For example, specify different libraries, or different versions of libraries than the ones found in the public catalog. You can have multiple clones of vcpkg on a single machine. Each one may be set to produce a custom collection of libraries, with your preferred compilation switches. Each clone is a self-contained environment with its own copy of vcpkg.exe that operates only on its own hierarchy. vcpkg isn't added to any environment variables, and has no dependency on the Windows Registry or Visual Studio.
Sources, not binaries
For libraries in the Windows catalog, vcpkg downloads sources instead of binaries1. It compiles those sources using the most recent version of Visual Studio that it can find. In C++, it's important that both your application code and any libraries you use are compiled by the same compiler, and compiler version. By using vcpkg, you eliminate or at least greatly reduce the potential for mismatched binaries and the problems they can cause. In teams that are standardized on a specific version of a compiler, one team member can use vcpkg to download sources and compile a set of binaries. Then they can use the export command to zip up the binaries and headers for other team members. For more information, see Export compiled binaries and headers below.
You can also create a vcpkg clone that has private libraries in the ports collection. Add a port that downloads your prebuilt binaries and headers. Then, write a portfile.cmake file that simply copies those files to the preferred location.
1Note: sources are unavailable for some proprietary libraries. In these cases, vcpkg downloads compatible prebuilt binaries.
Installation
Clone the vcpkg repo from GitHub: https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg. You can download to any folder location you prefer.
Run the bootstrapper in the root folder:
- bootstrap-vcpkg.bat (Windows)
- ./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh (Linux, MacOS)
Search the list of available libraries
To see what packages are available, at the command prompt type: vcpkg search
This command enumerates the control files in the vcpkg/ports subfolders. You'll see a listing like this:
You can filter on a pattern, for example vcpkg search ta:
Install a library on your local machine
After you get the name of a library by using vcpkg search, you use vcpkg install to download the library and compile it. vcpkg uses the library's portfile in the ports directory. If no triplet is specified, vcpkg will install and compile for the default triplet for the target platform: x86-windows, x64-linux.cmake, or x64-osx.cmake.
For Linux libraries, vcpkg depends on gcc being installed on the local machine. On MacOS, vcpkg uses Clang.
When the portfile specifies dependencies, vcpkg downloads and installs them too. After downloading, vcpkg builds the library by using the same build system the library uses. CMake and (on Windows) MSBuild projects are preferred, but MAKE is supported, along with any other build system. If vcpkg can't find the specified build system on the local machine, it downloads and installs it.
For CMAKE projects, use CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE to make libraries available with find_package(). For example:
List the libraries already installed
After you've installed some libraries, you can use vcpkg list to see what you have:
Integrate with Visual Studio (Windows)
Per-user
Run vcpkg integrate install to configure Visual Studio to locate all vcpkg header files and binaries on a per-user basis. There's no need for manual editing of VC++ Directories paths. If you have multiple clones, the clone you run this command from becomes the new default location.
Now you can #include headers simply by typing the folder/header, and autocomplete assists you. No additional steps are required for linking to libs or adding project references. The following illustration shows how Visual Studio finds the azure-storage-cpp headers. vcpkg places its headers in the /installed subfolder, partitioned by target platform. The following diagram shows the list of include files in the /was subfolder for the library:
Per project
If you need to use a specific version of a library that's different from the version in your active vcpkg instance, follow these steps:
- Make a new clone of vcpkg
- Modify the portfile for the library to obtain the version you need
- Run vcpkg install <library>.
- Use vcpkg integrate project to create a NuGet package that references that library on a per-project basis.
Integrate with Visual Studio Code (Linux/MacOS)
Run vcpkg integrate install to configure Visual Studio Code on Linux/MacOS. This command sets the location of the vcpkg enlistment and enables IntelliSense on source files.
Target Linux from Windows via WSL
You can produce Linux binaries on a Windows machine by using the Windows Subsystem for Linux, or WSL. Follow the instructions to Set up WSL on Windows 10, and configure it with the Visual Studio extension for Linux. It's okay to put all your built libraries for Windows and Linux into the same folder. They're accessible from both Windows and WSL.
Export compiled binaries and headers
It's inefficient to make everyone on a team download and build common libraries. A single team member can use the vcpkg export command to create a common zip file of the binaries and headers, or a NuGet package. Then, it's easy to share it with other team members.
Update/upgrade installed libraries
The public catalog is kept up to date with the latest versions of the libraries. To determine which of your local libraries are out-of-date, use vcpkg update. When you're ready to update your ports collection to the latest version of the public catalog, run the vcpkg upgrade command. It automatically downloads and rebuilds any or all of your installed libraries that are out of date.
By default, the upgrade command only lists the libraries that are out of date; it doesn't upgrade them. To actually upgrade the libraries, use the --no-dry-run option.
Upgrade Options
- --no-dry-run Perform the upgrade; when not specified, the command only lists the out-of-date packages.
- --keep-going Continue installing packages even if one fails.
- --triplet <t> Set the default triplet for unqualified packages.
- --vcpkg-root <path> Specify the vcpkg directory to use instead of current directory or tool directory.
Upgrade example
The following example shows how to upgrade only specified libraries. vcpkg automatically pulls in dependencies as necessary.
Contribute new libraries
You can include any libraries you like in your private ports collection. To suggest a new library for the public catalog, open an issue on the GitHub vcpkg issue page.
Remove a library
Type vcpkg remove to remove an installed library. If any other libraries depend on it, you're asked to rerun the command with --recurse, which causes all downstream libraries to be removed.
Customize vcpkg
You can modify your clone of vcpkg in any way you like. You can even create multiple vcpkg clones, then modify the portfiles in each one. That's a simple way to obtain specific library versions, or to specify particular command-line parameters. For example, in an enterprise, individual groups of developers might work on software that has a set of dependencies specific to their group. The solution is to set up a clone of vcpkg for each team. Then, modify the clones to download the library versions and set the compilation switches that each team needs.
Uninstall vcpkg
Just delete the vcpkg directory. Deleting this directory uninstalls the vcpkg distribution, and all the libraries that vcpkg has installed.
Send feedback about vcpkg
Use the vcpkg contact --survey command to send feedback to Microsoft about vcpkg, including bug reports and suggestions for features.
Microsoft Update Manager Mac
The vcpkg folder hierarchy
All vcpkg functionality and data is self-contained in a single directory hierarchy, called an 'instance'. There are no registry settings or environment variables. You can have any number of instances of vcpkg on a machine, and they won't interfere with each other.
The contents of a vcpkg instance are:
- buildtrees -- contains subfolders of sources from which each library is built
- docs -- documentation and examples
- downloads -- cached copies of any downloaded tools or sources. vcpkg searches here first when you run the install command.
- installed-- Contains the headers and binaries for each installed library. When you integrate with Visual Studio, you're essentially telling it add this folder to its search paths.
- packages -- Internal folder for staging between installs.
- ports -- Files that describe each library in the catalog, its version, and where to download it. You can add your own ports if needed.
- scripts -- Scripts (cmake, powershell) used by vcpkg.
- toolsrc -- C++ source code for vcpkg and related components
- triplets -- Contains the settings for each supported target platform (for example, x86-windows or x64-uwp).
Command-line reference
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| vcpkg search [pat] | Search for packages available to install |
| vcpkg install <pkg>.. | Install a package |
| vcpkg remove <pkg>.. | Uninstall a package |
| vcpkg remove --outdated | Uninstall all out-of-date packages |
| vcpkg list | List installed packages |
| vcpkg update | Display list of packages for updating |
| vcpkg upgrade | Rebuild all outdated packages |
| vcpkg hash <file> [alg] | Hash a file by specific algorithm, default SHA512 |
| vcpkg integrate install | Make installed packages available user-wide. Requires admin privileges on first use |
| vcpkg integrate remove | Remove user-wide integration |
| vcpkg integrate project | Generate a referencing NuGet package for individual VS project use |
| vcpkg export <pkg>.. [opt].. | Export a package |
| vcpkg edit <pkg> | Open up a port for editing (uses %EDITOR%, default 'code') |
| vcpkg create <pkg> <url> [archivename] | Create a new package |
| vcpkg cache | List cached compiled packages |
| vcpkg version | Display version information |
| vcpkg contact --survey | Display contact information to send feedback. |
Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| --triplet <t> | Specify the target architecture triplet. (default: %VCPKG_DEFAULT_TRIPLET%, see also vcpkg help triplet) |
| --vcpkg-root <path> | Specify the vcpkg root directory (default: %VCPKG_ROOT%) |
Applies to: Configuration Manager (current branch)
This article describes how to deploy and maintain the Configuration Manager client on Mac computers. To learn about what you have to configure before deploying clients to Mac computers, see Prepare to deploy client software to Macs.
When you install a new client for Mac computers, you might have to also install Configuration Manager updates to reflect the new client information in the Configuration Manager console.
In these procedures, you have two options for installing client certificates. Read more about client certificates for Macs in Prepare to deploy client software to Macs.
Use Configuration Manager enrollment by using the CMEnroll tool. The enrollment process doesn't support automatic certificate renewal. Re-enroll the Mac computer before the installed certificate expires.
Use a certificate request and installation method that is independent from Configuration Manager.
Important
To deploy the client to devices running macOS Sierra, correctly configure the Subject name of the management point certificate. For example, use the FQDN of the management point server.
Configure client settings
Use the default client settings to configure enrollment for Mac computers. You can't use custom client settings. To request and install the certificate, the Configuration Manager client for Mac requires the default client settings.
In the Configuration Manager console, go to the Administration workspace. Select the Client Settings node, and then select Default Client Settings.
On the Home tab of the ribbon, in the Properties group, choose Properties.
Select the Enrollment section, and then configure the following settings:
Allow users to enroll mobile devices and Mac computers: Yes
Enrollment profile: Choose Set Profile.
In the Mobile Device Enrollment Profile dialog box, choose Create.
In the Create Enrollment Profile dialog box, enter a name for this enrollment profile. Then configure the Management site code. Select the Configuration Manager primary site that contains the management points for these Mac computers.
Note
If you can't select the site, make sure that you configure at least one management point in the site to support mobile devices.
Choose Add.
In the Add Certification Authority for Mobile Devices window, select the certification authority server that issues certificates to Mac computers.
In the Create Enrollment Profile dialog box, select the Mac computer certificate template that you previously created.
Select OK to close the Enrollment Profile dialog box, and then the Default Client Settings dialog box.
Tip
If you want to change the client policy interval, use Client policy polling interval in the Client Policy client setting group.
The next time the devices download client policy, Configuration Manager applies these settings for all users. To initiate policy retrieval for a single client, see Initiate policy retrieval for a Configuration Manager client.
In addition to the enrollment client settings, make sure that you have configured the following client device settings:
Hardware inventory: Enable and configure this feature if you want to collect hardware inventory from Mac and Windows client computers. For more information, see How to extend hardware inventory.
Compliance settings: Enable and configure this feature if you want to evaluate and remediate settings on Mac and Windows client computers. For more information, see Plan for and configure compliance settings.
For more information, see How to configure client settings.
Download the client for macOS
Download the macOS client file package, Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager - macOS Client (64-bit). Save ConfigmgrMacClient.msi to a computer that runs Windows. This file isn't on the Configuration Manager installation media.
Run the installer on the Windows computer. Extract the Mac client package, Macclient.dmg Microsoft remote desktop mac vnc. , to a folder on the local disk. The default path is
C:Program FilesMicrosoftSystem Center Configuration Manager for Mac client.Copy the Macclient.dmg file to a folder on the Mac computer.
On the Mac computer, run Macclient.dmg to extract the files to a folder on the local disk.
In the folder, make sure that it contains the following files:
Ccmsetup: Installs the Configuration Manager client on your Mac computers using CMClient.pkg
CMDiagnostics: Collects diagnostic information related to the Configuration Manager client on your Mac computers
CMUninstall: Uninstalls the client from your Mac computers
CMAppUtil: Converts Apple application packages into a format that you can deploy as a Configuration Manager application
CMEnroll: Requests and installs the client certificate for a Mac computer so that you can then install the Configuration Manager client
Enroll the Mac client
Enroll individual clients with the Mac computer enrollment wizard.
To automate enrollment for many clients, use the CMEnroll tool.
Enroll the client with the Mac computer enrollment wizard
Microsoft Picture Manager Mac Download
After you install the client, the Computer Enrollment wizard opens. To manually start the wizard, select Enroll from the Configuration Manager preference page.
On the second page of the wizard, provide the following information:
User name: The user name can be in the following formats:
domainname. For example:contosomnorthuser@domain. For example:mnorth@contoso.comImportant
When you use an email address to populate the User name field, Configuration Manager automatically populates the Server name field. It uses the default name of the enrollment proxy point server and the domain name of the email address. If these names don't match the name of the enrollment proxy point server, fix the Server name during enrollment.
The user name and corresponding password must match an Active Directory user account that has Read and Enroll permissions on the Mac client certificate template.
Server name: The name of the enrollment proxy point server.
Client and certificate automation with CMEnroll
Use this procedure for automation of client installation and requesting and enrollment of client certificates with the CMEnroll tool. To run the tool, you must have an Active Directory user account.
On the Mac computer, navigate to the folder where you extracted the contents of the Macclient.dmg file.
Enter the following command:
sudo ./ccmsetupWait until you see the Completed installation message. Although the installer displays a message that you must restart now, don't restart, and continue to the next step.
From the Tools folder on the Mac computer, type the following command:
sudo ./CMEnroll -s <enrollment_proxy_server_name> -ignorecertchainvalidation -u '<user_name>'After the client installs, the Mac Computer Enrollment wizard opens to help you enroll the Mac computer. For more information, see Enroll the client by using the Mac computer enrollment wizard.
Example: If the enrollment proxy point server is named server02.contoso.com, and you grant contosomnorth permissions for the Mac client certificate template, type the following command:
sudo ./CMEnroll -s server02.contoso.com -ignorecertchainvalidation -u 'contosomnorth'Note
If the user name includes any of the following characters, enrollment fails:
<>'+=,. Use an out-of-band certificate with a user name that doesn't include these characters.Notes:.To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use Search. Buy microsoft word 2016. For users with mobility or vision disabilities, keyboard shortcuts can be easier than using the touchscreen, and are an essential alternative to using a mouse.
For a more seamless user experience, script the installation steps. Then users only have to supply their user name and password.
Type the password for the Active Directory user account. When you enter this command, it prompts for two passwords. The first password is for the super user account to run the command. The second prompt is for the Active Directory user account. The prompts look identical, so make sure that you specify them in the correct sequence.
Wait until you see the Successfully enrolled message.
To limit the enrolled certificate to Configuration Manager, on the Mac computer, open a terminal window and make the following changes:
Enter the command
sudo /Applications/Utilities/Keychain Access.app/Contents/MacOS/Keychain AccessIn the Keychain Access window, in the Keychains section, choose System. Then in the Category section, choose Keys.
Expand the keys to view the client certificates. Find the certificate with a private key that you installed, and open the key.
On the Access Control tab, choose Confirm before allowing access.
Browse to /Library/Application Support/Microsoft/CCM, select CCMClient, and then choose Add.
Choose Save Changes and close the Keychain Access dialog box.
Restart the Mac computer.
To verify that the client installation is successful, open the Configuration Manager item in System Preferences on the Mac computer. Also update and view the All Systems collection in the Configuration Manager console. Confirm that the Mac computer appears in this collection as a managed client.
Tip
Microsoft Manager Mac Free
To help troubleshoot the Mac client, use the CMDiagnostics tool included with the Mac client package. Use it to collect the following diagnostic information:
- A list of running processes
- The Mac OS X operating system version
- Mac OS X crash reports relating to the Configuration Manager client including CCM*.crash and System Preference.crash.
- The Bill of Materials (BOM) file and property list (.plist) file created by the Configuration Manager client installation.
- The contents of the folder /Library/Application Support/Microsoft/CCM/Logs.
The information collected by CmDiagnostics is added to a zip file that is saved to the desktop of the computer and is named cmdiag-<hostname>-<datetime>.zip
Manage certificates external to Configuration Manager
Microsoft Customer Manager Mac
You can use a certificate request and installation method independent from Configuration Manager. Use the same general process, but include the following additional steps:
When you install the Configuration Manager client, use the MP and SubjectName command-line options. Enter the following command:
sudo ./ccmsetup -MP <management point internet FQDN> -SubjectName <certificate subject name>. The certificate subject name is case-sensitive, so type it exactly as it appears in the certificate details.Example: The management point's internet FQDN is server03.contoso.com. The Mac client certificate has the FQDN of mac12.contoso.com as a common name in the certificate subject. Use the following command:
sudo ./ccmsetup -MP server03.contoso.com -SubjectName mac12.contoso.comIf you have more than one certificate that contains the same subject value, specify the certificate serial number to use for the Configuration Manager client. Use the following command:
sudo defaults write com.microsoft.ccmclient SerialNumber -data '<serial number>'.For example:
sudo defaults write com.microsoft.ccmclient SerialNumber -data '17D4391A00000003DB'
Renew the Mac client certificate
This procedure removes the SMSID. The Configuration Manager client for Mac requires a new ID to use a new or renewed certificate.
Microsoft Office Picture Manager Mac
Important
Microsoft Picture Manager Mac Free Download
After you replace the client SMSID, when you delete the old resource in the Configuration Manager console, you also delete any stored client history. For example, hardware inventory history for that client.
Microsoft Mac Software
Create and populate a device collection for the Mac computers that must renew the computer certificates.
In the Assets and Compliance workspace, start the Create Configuration Item Wizard.
On the General page of the wizard, specify the following information:
Name: Remove SMSID for Mac
Type: Mac OS X
On the Supported Platforms page, select all Mac OS X versions.
On the Settings page, select New. In the Create Setting window, specify the following information:
Name: Remove SMSID for Mac
Setting type: Script
Data type: String
In the Create Setting window, for Discovery script, select Add script. This action specifies a script to discover Mac computers configured with an SMSID.
In the Edit Discovery Script window, enter the following shell script:
Choose OK to close the Edit Discovery Script window.
In the Create Setting window, for Remediation script (optional), choose Add script. This action specifies a script to remove the SMSID when it's found on Mac computers.
In the Create Remediation Script window, enter the following shell script:
Choose OK to close the Create Remediation Script window.
On the Compliance Rules page, choose New. Then in the Create Rule window, specify the following information:
Name: Remove SMSID for Mac
Selected setting: Choose Browse and then select the discovery script that you previously specified.
In the following values field: The domain/default pair of (com.microsoft.ccmclient, SMSID) does not exist.
Enable the option to Run the specified remediation script when this setting is noncompliant.
Complete the wizard.
Create a configuration baseline that contains this configuration item. Deploy the baseline to the target collection.
For more information, see How to create configuration baselines.
After you install a new certificate on Mac computers that have the SMSID removed, run the following command to configure the client to use the new certificate: